
You can connect to that console using virsh console vmname The above commands should work with most Linux distributions, though in some cases it may not. It is possible to use a “serial” console setting in the virt-install command, by removing the -vnc and adding -graphics none \

There are a lot of ways to connect to your VM. This specific command will also create a VNC console, which we can connect to to perform the installation. The above command will perform the necessary creation steps, create teh VM definition files, generate a qcow2 file for the hard disk, and then kick-off the installation. disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/new-vm.qcow2,size=20,format=qcow2 \
INSTALL LINUX ON MAC MINI INSTALL
Once wget is done, we should have the same ISO file we used to install Ubuntu on the VM host! Start installation $ sudo virt-install -name new-vm \ To pull our ISO file, $ cd /var/lib/libvirt/boot/ In our example, we are going to pull down the Ubuntu Server installation ISO, and create a VM from it. We aren’t going to do that, and instead install via an ISO file. It is possible to install your VM directly from a web location, or to pull down a pre-built image for your VM. We can use these same tools to change the host from using DHCP, or visa versa. Here, I am given the ability to hit Enter to confirm the new configuration, but if the config breaks networking, in 120 seconds, the configuration will be rolled back. Press ENTER before the timeout to accept the new configuration Warning: Stopping rvice, but it can still be activated by: The command that works better for this, is netplay try which looks like this: $ sudo netplan try The downside to this command is if your config is syntactically correct, but breaks networking, you’ll need to console into your Mac mini (read, more displays & keyboards) to fix this. This command will apply the netplan config, unless there is a syntax error. To apply this configuration, we could run netplan apply The name of the bridge, br15 is our choice, but we will want to use a name that makes sense. Or if we want to keep using DHCP: # This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
INSTALL LINUX ON MAC MINI UPDATE
To create our bridge, we update this file to look like this: # This is the network config written by 'subiquity' If you configured your VM host to use DHCP, it may look closer to this: # This is the network config written by 'subiquity'

This file is /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml # This is the network config written by 'subiquity' Netplan can do a lot more than just build bridges for us, so definitely cehck out some of the examples on their site.īelow is the original Netplan file, generated by the initial Ubuntu install on our host.

With Netplan, we are able to define networking on our host using YAML, which is awesome. Ubuntu 20.04 (and 18.04) make this very very easy for us to do this, with something called Netplan.
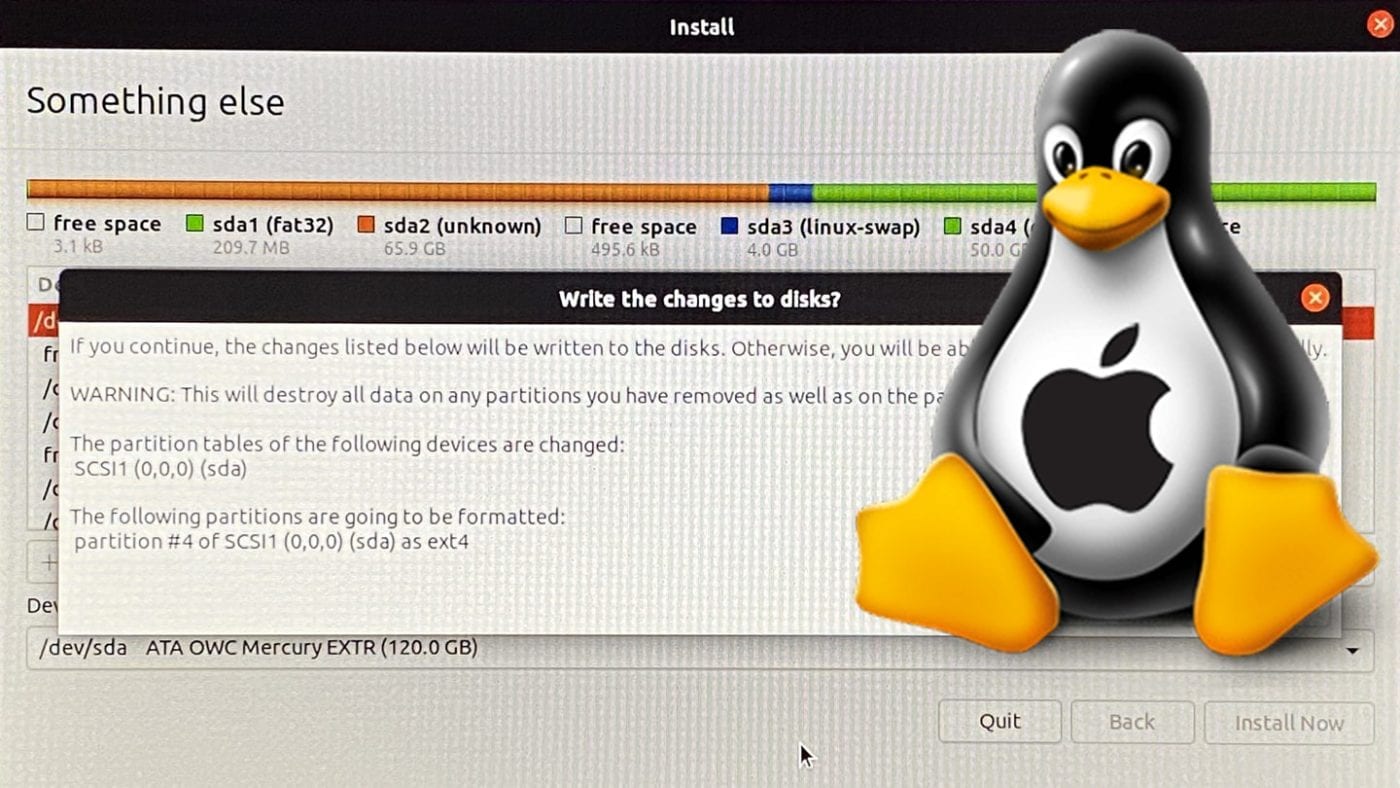
In our case, we are going to create a network bridge, that will allow us to “plug” our VMs directly into the same network our VM host is plugged into. There are a ton of ways to go about this we could create a local network, create network definitions via virsh, etc. Configure the Network Bridgeīefore we get started deploying VMs to our new KVM host, we need to get networking configured for our VMs. This part we will cover the configuration of a network bridge, and installing a Linux guest.
INSTALL LINUX ON MAC MINI SERIES
This is part 2 of a series for getting KVM/Libvirt up and running on a Mac mini. Getting Ubuntu & KVM installed on a Mac mini for virtualization.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
